Top 5 best NRI Investment Options for Long & Short term in India
NRI deposits climbed to $6.97 billion in April-July 2015, from $4.71 billion a year ago, according to the RBI Bulletin for September 2015.
Outstanding NRI deposits exceeded $120 billion. More and more Indians living abroad are turning homeward to park their surplus money.
An NRI is spoilt for choices when it comes to NRI investment options in India, both in the long-term and the short-term sections.
Best NRI investment options
An NRI can invest in India through two different routes: one is the “automatic route,” where no government approvals are required, and the other is the “government route,” where an NRI needs to take approval from the government before making an investment.
Also, an NRI investment opportunity will specify whether it can be repatriated or not. Repatriation refers to a condition when the amount can be transferred to the source.
Some of the investment options are government securities, treasury bills, mutual funds, bonds issued by PSU, certificate of deposits, perpetual bonds, stocks, ETF, money market mutual funds, real estate property, company deposits and more.
Popular post: 15 best investment options in India
But for money to be parked for short term or long-term investments, an NRI needs to have any one of three following types of banks accounts:
- Non-Resident Ordinary Rupee Account (NRO) – This account is not suitable if you want to transfer Indian earnings abroad freely as it has USD1million limit .It also needs tax paid certificate from certified CA before repatriation. Foreign funds can also be deposited in this account. The interest earned through this account is liable to be taxed in India. The interest is subject to income tax deduction at source at 30%, plus applicable surcharge and education cess, says an article published in Money Control in November 2012. It should primarily be used for depositing/managing your earnings in India.
- Non-Resident External Rupee Account (NRE) – In this type of account, your funds in foreign currency are converted into Indian rupees and the rate prevailing at the time of conversion is applicable. Funds in the NRE account as well as the principal amount and interest are completely repatriable. You can open an NRE savings, recurring or fixed deposit account.
- Foreign Currency Non-Resident Bank Deposits (FCNR) – These are term deposit or fixed deposit accounts, where you can deposit your money in foreign currency. This account can help you avoid the fluctuations in the exchange rate. The account can be opened jointly with an Indian resident. The deposits must be made for a minimum maturity period of one year and maximum maturity period of 5 years. The interest earned under this account is tax free, while the principal amount is taxed under wealth tax. Interest earned on FCNR fixed deposit is close to 1.5-2.0%.
Related: Difference between NRE and NRO account
NRI Fixed Income Investment Opportunities
Apart from opening a fixed deposit FCNR or NRE accounts, here are some investment opportunities that an NRI can consider for short term and long term growth.
1. National Pension Scheme – This enables the policyholder to save towards creating a corpus and also lets him open an annuity post retirement.
An NPS account can only be opened by individuals, and not jointly. After the initial form is submitted, a Permanent Retirement Account Number (PRAN) is allotted.
Thereafter, the transaction may be made online. Investments in NPS can only be done by a Citizen of India living in India or an NRI who holds an Indian citizenship.
If at any point, an NRI gives up his citizenship, the account is closed. The minimum contribution being Rs 500 (in Tier-1 accounts), NPS offers many opportunities for flexible investment options with a range of funds to choose from.
However, it is mandatory to invest 40 percent of the investment in annuity scheme on a regular retirement.
NRIs can contribute in the NPS through fund transfers from their NRE/NRO account. Individual contributions to the NPS are subject to a ceil1ing of 10% of the gross national income.
Investors have the right to choose the type of investment they make, be it government securities, equity related or other fixed income options. These contribution are eligible for a tax deduction of up to Rs 1,50,000, along with the contributions to other schemes.
An additional deduction of Rs 50,000 is specifically allowed for the contributions towards NPS under section 80CCD(1B). Also, any lump sum amount or annual receipts withdraw from an NPS are treated as taxable income.
The image below shows the latest data available on the rate of return on NPS schemes of various banks:
2. Fixed Deposits – An NRE fixed deposit or an FCNR account is preferable. You can earn upto 8.5 percent return on an NRE fixed deposit, ever since the RBI linked the same with LIBOR.
Also, the interest on NRE fixed deposits and FCNR accounts is tax free in India. The rate of return on FCNR accounts differs according to the currency you deposit.
You can also open an NRO FD account, but the interest earned cannot be repatriated and taxable at source.
The interest rate for an FCNR account depends on the currency. Interest earned on an NRO fixed deposit account ranges from 4% to 7.75%, depending upon the maturity period of the deposit.
Becoming an NRI – 9 Things to do before becoming NRI
3. Certificates of Deposit (CDs) – This is a non-negotiable money market instrument issued in demat form or as promissory notes.
It has a maturity of not less than 7 days and not more than 1 year. CDs are much like time deposits, except they tend to be more liquid.
NRIs can also subscribe to CDs but only on a repatriable basis. The rate on return is generally higher than for bank fixed deposits and this sis common NRI investment option used by many of my friends. But I prefer fixed deposits and PPF instead.
4. Bonds – Perpetual bonds are bonds that can never be redeemed. Investors are eligible to receive fixed interest on such bonds.
Such bonds can be issued by a company or government institutions seeking long-term investments. Perpetual bonds are also issued by banks under Tier-1 capital.
In March 2015, banks offered coupon rates between 9.48% and 10.75% but they lock your principal amount for quite some time.
Useful: Introduction to Bonds, coupons and types of bonds
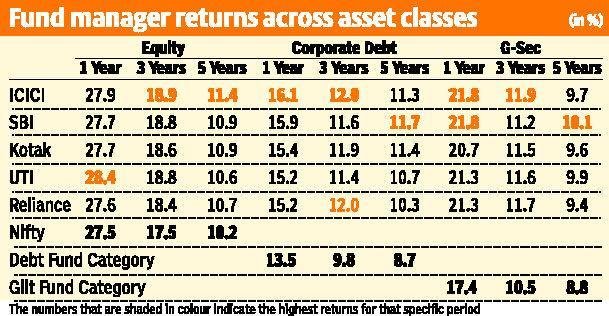
Mutual Funds – Mutual funds can be both1 equity as well as debt mutual funds.
Debt funds basically invest in fixed income securities, which include government securities, treasury bills, corporate bonds, money market instruments and more.
The one major advantage with debt mutual funds is that it is managed by experienced fund managers. Also, these are fairly liquid. You can withdraw money as and when you want and you will receive the same in your bank account in about 3-4 business days.
These funds provide safety of capital. While returns are low, given the safety of capital, they are preferred over equity mutual funds in the short term.
For mid-term, investing in hybrid funds is advisable, which includes both debt and equity investments.





Call Us : +91 93310 16791
Email: inssd@yahoo.co.in